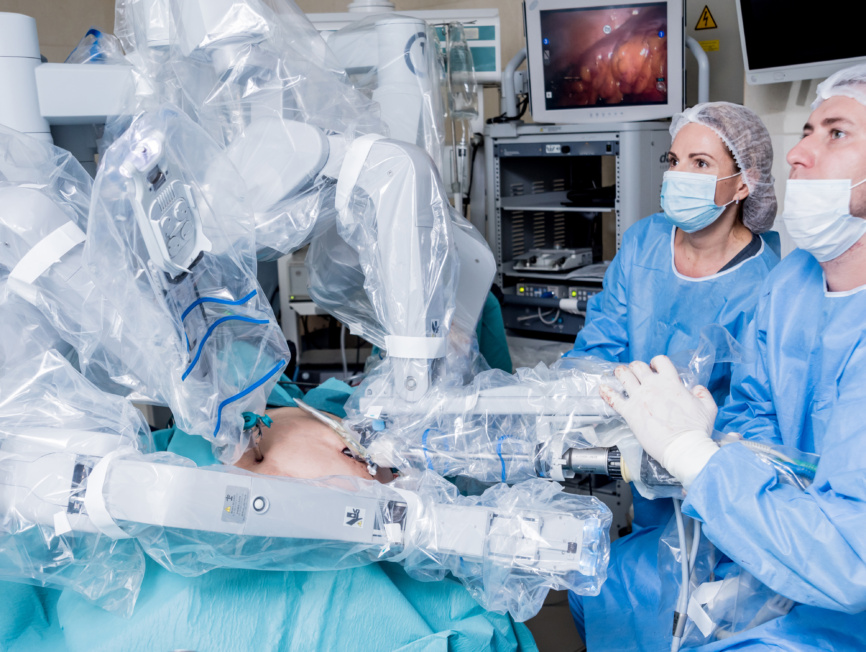
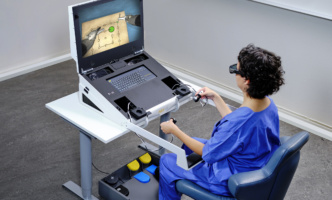
Educational Products for Healthcare Professionals
With our ready-to-use simulators and evidence-based customizable curricula, healthcare professionals and teams can elevate their proficiency, promote professional growth, and ultimately improve patient treatment and safety.